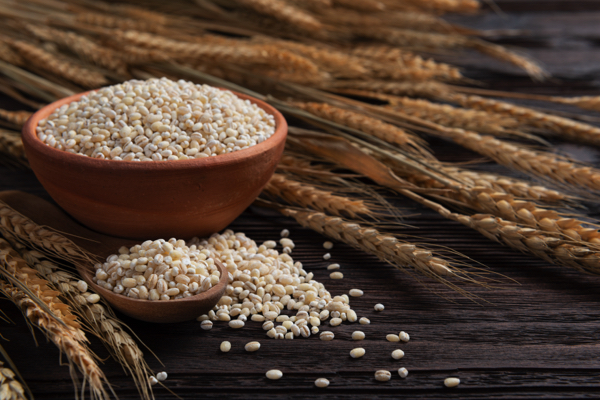
- Barley is one of the oldest cultivated grains, originating in Ethiopia and Southeast Asia some 10,000 years ago. It played a key role in ancient diets and remains a resilient global staple today.
- Rich in fiber, protein, B vitamins, minerals and antioxidants, barley can support heart health, digestion, blood sugar control and healthy weight management.
- Barley also helps lower LDL cholesterol, regulates blood pressure, promotes gut health and can aid in diabetes management with its low glycemic index.
- Barley contains gluten, making it unsafe for people with celiac disease. Its high fiber content also makes it unsuitable for people with IBS. Opt for organic barley to avoid pesticides (e.g., glyphosate) and heavy metals.
- Barley can be used to make soups, salads, porridge, baked goods and beverages. Common forms of barley include hulled, pearled and flour.
Nutrients and health benefits
Barley is a nutrient-dense whole grain, rich in the following:- Fiber, both soluble and insoluble, particularly beta-glucan, which supports heart health and digestion
- Protein, an essential nutrient for muscle repair and energy
- B vitamins, particularly B1 (thiamine) and B3 (niacin), which are needed for metabolism and neurological function
- Minerals, including selenium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron and zinc
- Antioxidants, such as lignans and ferulic acid, which help combat inflammation
- Supports digestive health – The high fiber content of barley supports digestion, prevents constipation and feeds beneficial gut bacteria.
- Lowers cholesterol – Beta-glucan binds to cholesterol, helping reduce LDL ("bad" cholesterol) levels.
- Balances blood sugar – Its low glycemic index makes barley excellent for diabetics or those managing insulin resistance.
- Promotes heart health – Magnesium and potassium help regulate blood pressure, while antioxidants reduce oxidative stress.
- Aids in weight management – Barley's satiating properties help control hunger and reduce overeating.
Culinary uses and recipes
Barley's chewy texture and nutty flavor make it a fantastic addition to many dishes. Common forms include:- Pearled barley (polished, cooks faster)
- Hulled barley (whole grain, more nutritious)
- Barley flakes (like oatmeal)
- Barley flour (used in bread and baked goods)
- Barley soup – A traditional dish in many cultures, such as Scotch broth (Scotland) and mushroom barley soup (Eastern Europe).
- Barley risotto – A fiber-rich twist on traditional risotto with mushrooms or vegetables.
- Barley salad – Mixed with roasted veggies, feta and a lemon dressing.
- Barley porridge – A warming breakfast, similar to oatmeal, topped with honey and nuts.
- Beverages – Used in beer brewing and even barley tea (mugicha in Japan).
More related stories:
Hexacosanol derived from barley sprouts helps lower cholesterol.
Barley being studied as a potential cure for diabetes.
Barley: Ancient grain with science-backed benefits for a healthy pregnancy.
Sources include: Brighteon.AI NaturalNews.com Brighteon.comHow Vitamins D and B12 could be the missing link in preventing dementia
By Cassie B. // Share
Idaho Legislature clears path for over-the-counter ivermectin sales
By Ava Grace // Share
Valerian: An ancient herbal remedy fit for modern times
By Ava Grace // Share
The ancient superfood revival: Discovering the healing power of Job’s tears
By Ava Grace // Share
Oats: A nutritional powerhouse for health and wellness
By Laura Harris // Share
Zelensky extends martial law again, delaying elections amid legitimacy concerns
By isabelle // Share
Trump’s tariff policies trigger global economic decoupling: Health Ranger warns of U.S. collapse
By finnheartley // Share
How Vitamins D and B12 could be the missing link in preventing dementia
By isabelle // Share