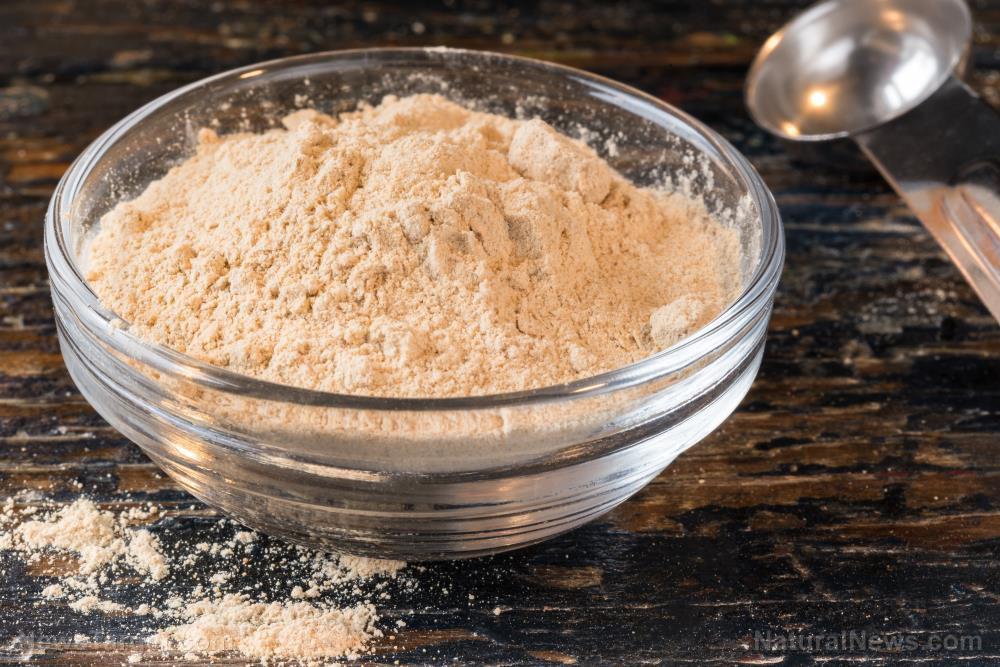
- Maca, or "Peruvian ginseng," has been cultivated in the Andes for over 2,000 years, initially domesticated around 1600 BCE. It was highly valued by the Inca civilization and used as currency before its decline post-Spanish conquest. Modern commercial interest in maca resurged in the late 1980s.
- Maca is rich source of essential vitamins and minerals, fiber and protein, including vitamin C, copper, iron and potassium. It also contains bioactive compounds like glucosinolates, alkaloids and sterols that are thought to support hormonal balance, enhance energy and improve overall well-being.
- Well-documented benefits of maca include regulating the menstrual cycle and alleviating menopausal symptoms in women, enhancing physical performance and stamina, improving mood and reducing stress, making it useful for mental health support.
- Maca is classified by root color (yellow, black, red), each believed to have distinct properties. The root is harvested after about seven months and can be ground into a powder with a nutty, malt-like flavor, suitable for various culinary uses such as in smoothies, energy bars and baked goods.
- From traditional Andean remedies to contemporary superfood trends, maca is used to boost energy, support hormonal health and enhance overall well-being. Its popularity continues to grow, and it is easily incorporated into various recipes and dietary supplements.
Brief history of maca
Maca's history is as rich as its flavor. Indigenous communities in the Andes have cultivated and utilized maca for over 2,000 years, primarily for its nutritional and medicinal properties. According to archaeological evidence, maca was first domesticated around 1600 BCE in the Junin plateau of central Peru. The plant was revered by the Inca civilization and was often used as a form of currency and tribute. However, with the Spanish conquest, maca's cultivation and use declined significantly. (Related: Maca root can increase libido and help treat sexual dysfunction.) The modern rediscovery of maca for commercial purposes occurred in the late 1980s on the Meseta de Bombón plateau, near Lake Junin in Peru. This rediscovery sparked a resurgence in scientific research and global interest in the root's health benefits. Maca is known by several common names, including Peruvian ginseng, Peruvian maca and maca root. The root itself is typically harvested after the plant has grown for about seven months. Maca roots are tuberous in shape, similar to a small turnip or radish. They can be yellow, red or black, with the yellow variety being the most common. Each color variation is believed to have slightly different properties and benefits. When dried and ground into a powder, maca has a slightly nutty and malt-like flavor, which can be subtly sweet or bitter, depending on the variety. In the high Andes, a traditional story is told of an Inca farmer who, after a particularly harsh winter, found his livestock struggling to survive. In desperation, he turned to the maca root, which had been largely ignored by his ancestors. He fed the maca to his animals, and to his amazement, they regained their strength and vitality. This anecdote highlights the long-standing belief in the restorative properties of maca and its potential to support overall health and well-being.Nutritional profile and health benefits
Maca is a powerhouse of essential nutrients and beneficial phytonutrients, making it a valuable addition to a healthy diet. It is rich in essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, copper, iron and potassium. Maca also contains a significant amount of fiber and protein, making it a nutritious option for those looking to boost their intake of these macronutrients. One of the most remarkable qualities of maca is its wealth of bioactive compounds, including glucosinolates, alkaloids and sterols. These compounds are believed to contribute to maca's many health benefits, which include supporting hormonal balance, enhancing energy levels and improving overall well-being. Maca has also been studied for its potential to alleviate a range of symptoms and conditions. One of the most well-documented benefits of maca is its ability to support hormonal balance, particularly in women. Research suggests that maca may help regulate the menstrual cycle and alleviate symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and mood swings. Another notable benefit of maca is its potential to enhance physical performance and stamina. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts often turn to maca for its energy-boosting properties, which may be attributed to its rich nutrient profile and adaptogenic properties. Maca has also been studied for its potential to improve mood and reduce stress. Some studies have shown that maca can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, making it a valuable tool for supporting mental health.Culinary uses and recipe ideas
Maca is incredibly versatile and can be incorporated into a variety of recipes. Here are a few suggestions:- Maca smoothie - Combine maca powder with almond milk, banana and honey for a nutrient-packed breakfast smoothie.
- Maca energy bars - Blend maca powder with dates, nuts and seeds for a homemade energy bar that can be enjoyed on the go.
- Maca latte - Whisk maca powder into a warm latte for a comforting and nourishing drink.
- Maca muffins - Add maca powder to your favorite muffin recipe for an extra boost of vitamins and minerals.
- Maca oatmeal - Stir maca powder into your morning oatmeal for a hearty and energizing start to your day.
More related stories:
Maca Gives Potential Relief for Migraine Sufferers. Maca: the perfect food for balancing our hormones. Maca Restores Sexual Health without Raising Hormone Levels. Maca is the ancient superfood of the Incas. Sources include: Brighteon.ai NaturalNews.com Brighteon.comVITAMIN D: the sunshine vitamin’s powerful role in COLON CANCER prevention
By Lance D Johnson // Share
The remarkable heart-friendly properties of avocados
By News Editors // Share
Science reshapes autism care by looking beyond the brain
By Olivia Cook // Share
Ancient hydrogen and magma ocean offer clues about Earth’s origins
By Willow Tohi // Share
Buckwheat: A gluten-free superfood for modern health
By Laura Harris // Share
Trump administration proposes $40 billion HHS cuts, shifts focus to disease surveillance
By Cassie B. // Share
CATTLE CRISIS: How a historic herd decline is shaking U.S. beef security
By willowt // Share
VITAMIN D: the sunshine vitamin's powerful role in COLON CANCER prevention
By ljdevon // Share
‘Toxic cocktail’: study finds almost 200 pesticides in European homes
By sdwells // Share
A financial coup: How the deep state is using manufactured crises to seize power
By newseditors // Share